发布时间:2024-04-09 发布者:admin 来源:行业动态 点击次数:2048
碳纤维石墨软毡一般由粘胶纤维、PAN纤维等原丝先经过非织造工艺制成毡子,再经过浸渍(主要是粘胶基需要浸渍)、预氧化、碳化、石墨化、裁剪,最终得到成品。
石墨软毡的成型主要在前端的非织造工序,非织造是一系列复杂工艺的合称,有多种因素会影响成品质量,例如:将纤维梳理成网时,PAN纤维或粘胶纤维细、轻、较干燥,在设备的机械作用下容易起静电,影响设备正常运行,因此需通过加抗静电剂等方式减少静电;铺网时,铺网方式有平行式、交叉式、组合式、垂直式等多种类型,铺网层数可达几十层;针刺加固时,可选用不同型号的刺针、不同的刺针排布方式、不同的针刺次数。
这些仅仅是非织造工艺中采用干法成网、针刺加固的一小部分,非织造还有多种不同的技术路线。
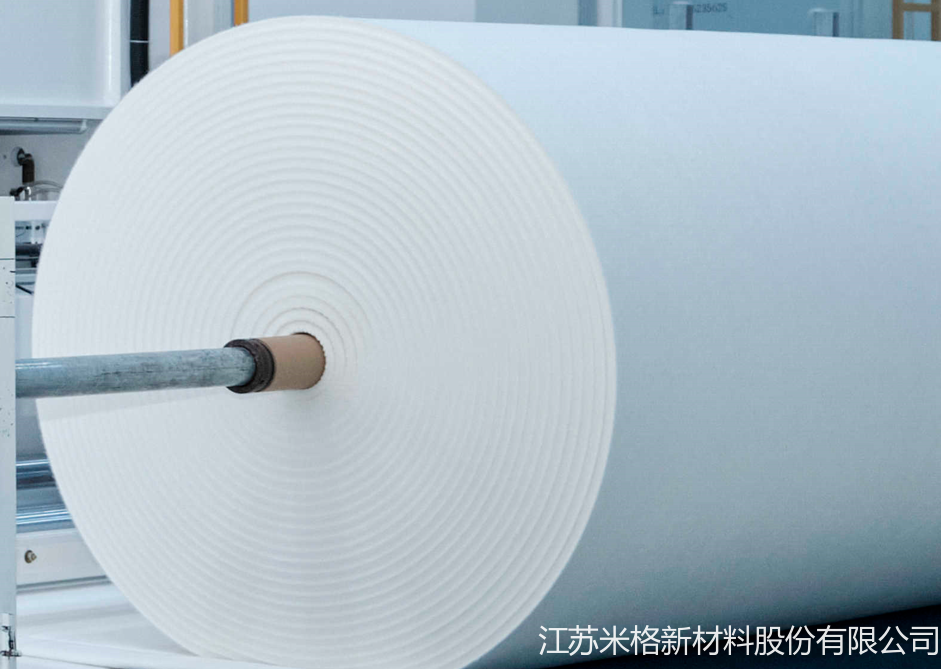
碳纤维石墨软毡通过非织造工艺成型
原丝纤维成型后,从预氧化开始由于毡子中的非碳元素一步步减少,石墨软毡相对于预氧化之前的毡子,其长度、宽度、厚度均会缩小。但未裁剪的石墨软毡仍然是一块面积巨大的材料,长度可达40m,宽度可达1.6m。
根据应用需求,对石墨软毡两端及两侧不平整部分进行裁剪,还可继续裁剪成面积合适的长方形软毡、圆形软毡,以及用于制作硬毡的各种形状坯料等。
从主要性能指标来看,石墨软毡的密度仅0.10g/cm³左右,约是水的密度的十分之一。石墨化之后的纤维本身就轻且细,再加上大量纤维之间形成小空间,让软毡的密度如此之低。
高纯/高效粘胶基石墨软毡的导热系数在1150℃约为0.10-0.15W/m·k,导热系数越低,保温性能越好。
硬毡的成型主要有软毡层压固化成型和湿法成型两种方式。常见的层压法制作碳纤维石墨硬毡以软毡为原料,生产工艺始于裁剪:从软毡上裁剪多块尺寸略大于最终所需成品硬毡尺寸的坯料。裁剪后浸渍树脂等粘结材料,并按所需硬毡厚度将浸渍后的坯料铺叠多层。
软毡生产中的浸渍主要是浸渍催化剂,让粘胶纤维在后续热处理中更稳定;而硬毡的浸渍主要是浸渍热固性树脂,在后续加热固化过程中,液态的树脂凝固,多层软毡与树脂紧密结合成型。
树脂+碳纤维石墨软毡,让材料在某些性能上能实现“1+1>2”的效果。浸渍了树脂的多层铺叠的软毡经过升温固化,已不像软毡一样可以卷起来,材料的密度、抗压强度也有所增加。
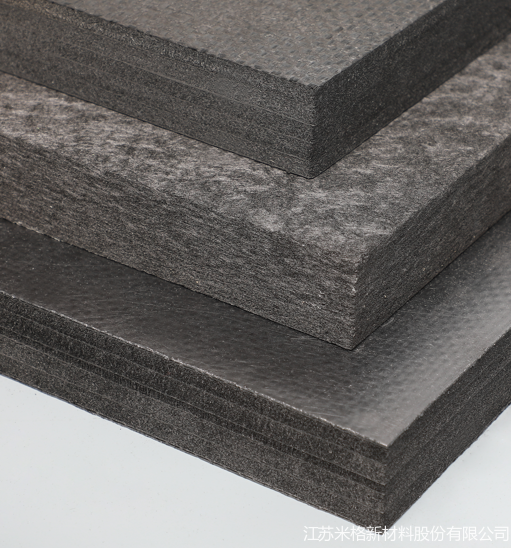
碳纤维石墨硬毡由多层软毡与树脂固化成型
但这还不是碳纤维石墨硬毡。因为其中的树脂含有大量碳以外的其他元素,需经过碳化、石墨化等工艺去除。
树脂中的碳作为基体,碳纤维石墨软毡作为增强体,它们复合在一起,最终成为硬毡这种复合材料。所以碳纤维石墨硬毡又称石墨硬质复合毡。
软毡纤维之间的小空间填充了树脂并固化后,半成品的密度必然高于原料软毡;碳化、石墨化之后,树脂失去了氢、氧原子等,密度又有所降低,但树脂中留下的碳让石墨硬毡密度仍然高于原料软毡的密度。硬毡密度约为0.13-0.25g/cm³。
石墨化之后硬毡的面积与固化之后半成品的面积几乎一样,一般小于裁剪前的原料软毡。
根据形状、表观要求,硬毡还需要进行机加工、涂层或贴碳布、石墨纸等处理。
相较于碳纤维石墨软毡,硬毡的导热系数略高,保温性不如软毡,但其使用寿命更长,例如在单晶炉中软毡的使用寿命约为6个月,而硬毡大概12个月更换一次。